Sparck NLP API
IssueLab is the knowledge platform for Candid, formerly known as the Foundation Center. Their goal is to collect, archive, and make accessible and useful “gray literature”— things like white papers, research reports, evaluations, and case studies. Most of the social sector produces and releases knowledge this way, but the sector lacks the formal channels and aggregators that academia has to make this content searchable, so that’s where IssueLab fits in.
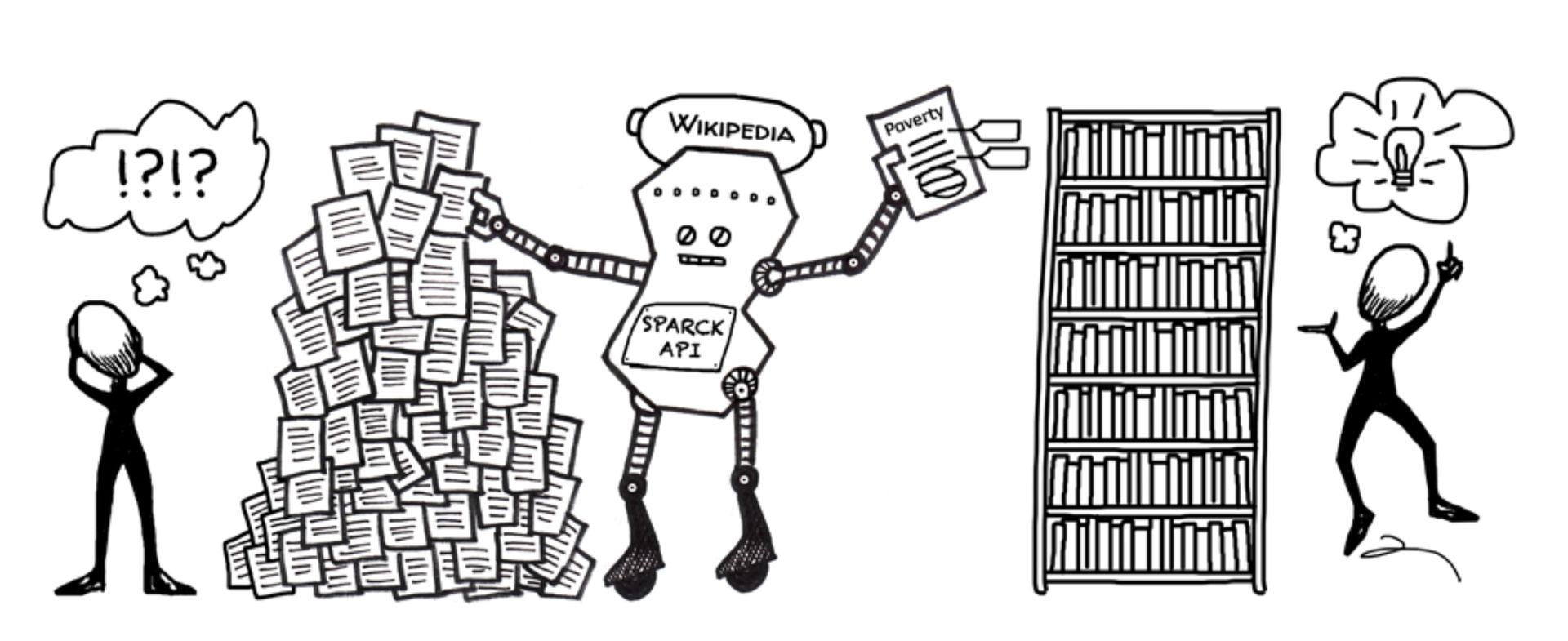
I worked on a team that built an API which uses natural language processing to help IssueLab add richer metadata to their collection for improved search results and exploration features. The API, called Sparck, accepts PDFs and processes them to produce keywords, key finding statements, and topics. It’s named for Karen Spärck Jones, a British pioneer in information retrieval.
On the backend it uses traditional NLP techniques like TF-IDF, as well as a novel technique we developed called WikiTopic. WikiTopic uses an ElasticSearch index of the Wikipedia corpus to produce relevant named topics for documents. (Keep in mind this was years before the development of large language models.)
Because of the long processing time to extract plain text from PDFs, the system works asynchronously using a job queue (implemented using Redis and RQ) and provides APIs and dashboards for the client to check on the status of documents and retrieve results.
I worked on the backend data engineering for the API (the queue system, API framework, Elastic instance, and deployment of all of the above using Ansible) as well as an online explainer and documentation for our clients. I also worked with the client to train them on the use and maintenance of the system.